"How to improve the efficiency of the enterprise?" and "Where to find added value?" Some answers may lie on the surface and have been in the arsenal of companies for a long time, such as “sell more and faster” and / or “cut the budget”, but not all solutions are obvious at first approximation. Today we will talk about one of them - Procurement Outsourcing (PO).
What is the difference between outsourcing and a third-party service
What determines the need for outsourcing
Procurement cycle
Maturity and development of procurement
Procurement organization forms
Global procurement outsourcing
Types of procurement outsourcing
Development of procurement outsourcing in Russia
What is the difference between outsourcing and a third-party service
The very concept of "outsourcing" (outer-source-using - the use of an external source and / or resource) appeared in Russia relatively recently. This is an approach of work organization, and it is often confused with obtaining an external service or outstaffing (“renting” employees).
The most accurate definition I met in Investopedia:
Outsourcing is the business practice of hiring a party outside a company to perform services and create goods that traditionally were performed in-house by the company's own employees and staff. Outsourcing is a practice usually undertaken by companies as a cost-cutting measure. The outsourcing service is usually long term. As such, it can affect a wide range of jobs, ranging from customer support to manufacturing to the back office.
Business traditions in Russia have changed dramatically over the past 30 years. For example, if we consider the cleaning function, then in Soviet enterprises in almost 100% of cases they were internal employees, then gradually the function began to be outsourced, but now in many organizations this is just a third-party service, since companies do not even consider the presence of cleaners in their own state. This also applied, for example, to the capital construction department (CCD) - now construction work, as a rule, is given to the third-party construction organization, since for non-core companies this is not only not the main activity, but also requires separate licensing. The same can be said about security services or cargo transportation.
What determines the need for outsourcing
The most common reason is that companies do not consider a certain function as a key in their activities, do not want to administer it (including diverting resources of topmanagement), but concentrate on their “heart of the profession”. As a result, this form of organization is more profitable, but rather not from the point of view of costs, but from the point of view of the overall economic effect for the company, as well as other (qualitative) performance indicators: raising the level of qualifications, improving the quality of data, etc. Examples of this type of outsourcing are, external IT support (1st and 2nd level) and accounting.
But there are opposite situations when the company has a need for development of an important internal function, but there is no opportunity to hire qualified personnel. For example, one large European company could not attract IT developers in Russia, as they preferred to pursue a career in the IT industry. As a result, the company paid $8 M yearly for outsourcing this function (not to be confused with outstaffing).
There may also be restrictions on the number of full-time employees.
Procurement cycle
The procurement process is a cycle from Analysis to Payment. The processes of spend and demand analysis, sourcing and negotiation with suppliers, contract and catalog management require high qualifications from buyers and are responsible for generating added value for the enterprise.
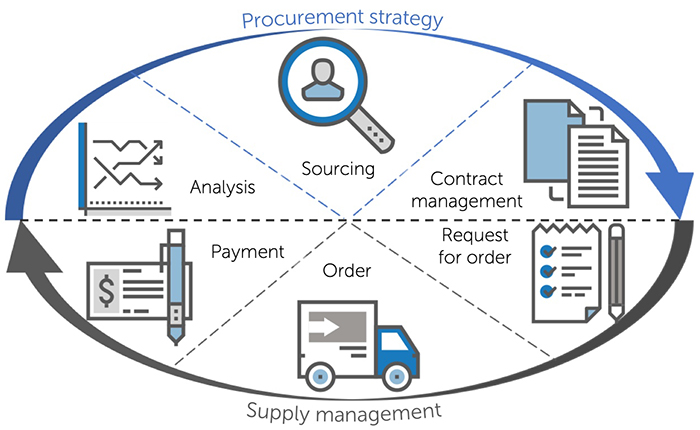
The processes of request creation and approval, orders to suppliers and acceptance, as well as payment and accounting require large resources for administration and ensure the receipt of materials or services on time and in full (OTIF).
Depending on the degree of criticality of procurement for the business and the procurement position of the company in the supplier market, the strategy and degree of elaboration at the stages of the cycle will be different.
Maturity and development of procurement
Our results of functional diagnostics of procurement by companies in various industries show that the average level of maturity and quality of the procurement process in Russia does not exceed 40% of the possible potential. This means that enterprises permanently lose huge funds and pass all their super-costs onto the end user, reducing their own competitiveness.
Why it happens:
- The management of the companies does not realize that Procurement can be organized differently. There is no clear example in a comparable field or industry. Relatively developed Procurement (60-70%) are available only in a number of companies with foreign management.
- Limited powers in Procurement and, as a result, low level of management: a large volume is purchased by “internal clients” themselves, who, even with insufficient understanding of the procurement process, would rather resort to the help of expensive external experts of their category than an internal procurement department (for example, purchases of media services ), there is no effect on the specification and consumption volume, Procurement are not involved in strategic projects (moreover, the coverage perimeter is only 30-40% of the potentially manageable volume of spend).
- There is no specialized education in procurement in Russia, and there are very few qualified specialists.
- Companies do not know how to assess the added value that Procurement brings. The reason for this is the low level of digitalization and master data, and the lack of developed methods and measuring tools.
- As a result, there is a low level of investment in the development of the Procurement function and the absence of any motivation for buyers.
Procurement organization forms
The forms of organizing the procurement process largely affect the final result. There are only three main forms:

Purchases are made by the "internal client".
An “internal client” can be almost any employee, such as an engineer, and even a CEO. This is a very common form of organization, the main motive of which is simplicity, low cost and the absence of additional employees (buyers). The fact is that “internal clients” are not qualified buyers, and as a rule, such purchases do not give an economic effect, and, in some cases, carry corruption risks. This form is appropriate for low-value purchases if there are established Policies and Procedures.
Procurement is carried out by a professional Buyer
This form of organization is most effective for strategic procurement, provided the teams are highly professional. Today many companies in Moscow offer salaries of $700-$900 for buyer and $1200 - $2000 for CPO. But we have already noted that there are very few qualified and honest buyers and their remuneration is usually 2 or more times higher than this level. In addition, in 65% of European companies, buyers receive% of the savings as a bonus, and this practice is starting to develop in Russia.
And the third form of organization - purchases is carried out by the Outsource company
This is a very new type of service on the Russian market, and in this article we will dwell on it in more detail.
Global procurement outsourcing
Today it is a new direction of procurement services that responds to the need for companies to improve the business-processes efficiency. Global Procurement Outsourcing Market in 2019 is estimated at $5-7 B and is growing by 13% annually. In the US, 28% of organizations already use the PO service, 90% of them assess this experience positively and plan to develop it.
Key players have over 1000 purchasing staff and tens of USD billions under management.
Types of procurement outsourcing
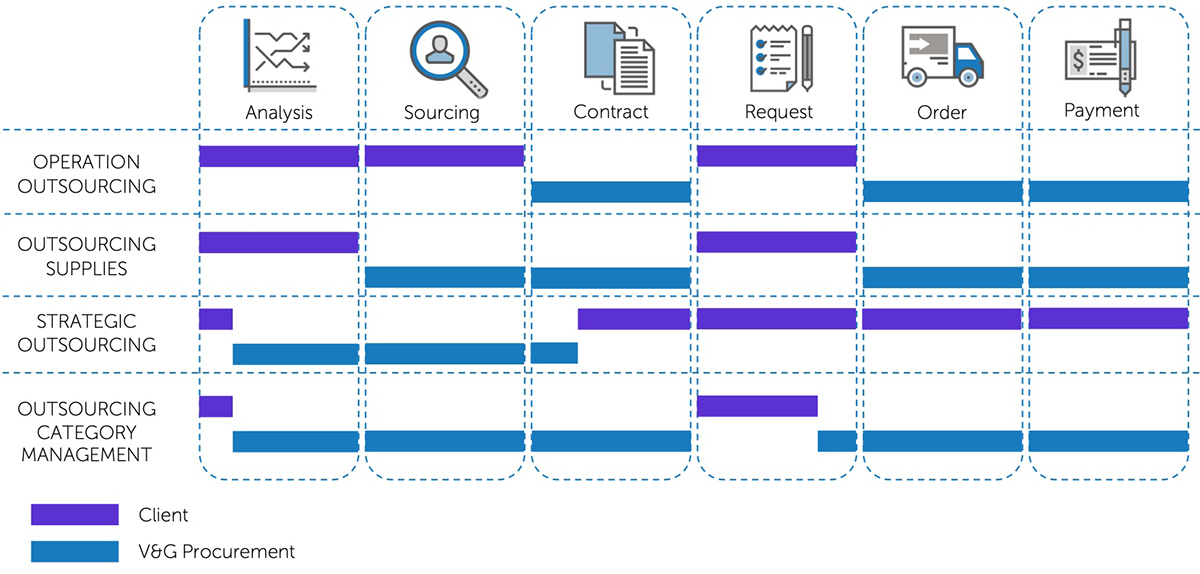
Outsourcing can cover both individual categories of materials and services, and individual stages of the procurement cycle, as well as individual processes (for example, outsourcing procurement analytics or calculating savings).
OPERATION OUTSOURCING
The Client transfers the administration of their suppliers and the commercial conditions to the Outsourcer. Based on the Requests from the Client, the Outsourcer purchases materials or services at his own expense and administers the supplies.
The client receives:
- Reduced administrative burden by reducing the number of direct contracts and the ability to focus on strategically important projects.
- Improving the terms of payment and cash flow due to consolidated payment based on the “one-stop shop” principle.
- Reduction of bureaucracy by optimizing workflow and overcoming internal requirements (for example, suppliers are not ready to provide the required payment delay, unlike an Outsourcer).
The Outsourcer's remuneration can be % of the purchase volume.
OUTSOURCING SUPPLIES
On the basis of Rerquests and Specifications from the Client, the Outsourcer searches for suppliers according to the "Open Book" principle. As in the scheme with Operation Outsourcing, all supplier administration lies with the Outsourcer.
In addition to the stated benefits of Operation Outsourcing, the Client can receive:
- Procurement Savings.
- Access to expertise.
- Reducing supplier risks and improving supply quality. Standardization of Specifications and Workflows.
- Improving compliance with the requirements of the beneficiaries. The outsourcer guarantees the integrity of the procurement process.
Outsourcing Supplies mainly provides low-value indirect purchases, which, however, can account for up to 20% of the company's spend.
Depending on the volume of purchases and whether the task is to save, the remuneration of the Outsourcer can either be calculated as a % of the purchase cost (in total within the budget of the Client company), or consist of a fixed part and % of the contractual procurement savings.
STRATEGIC OUTSOURCING
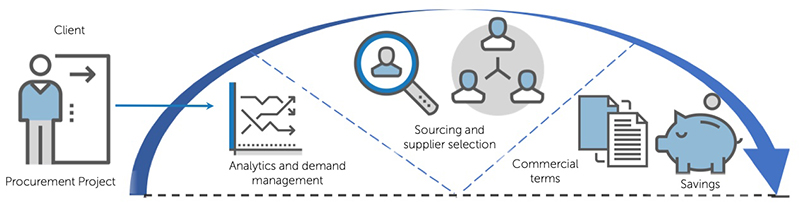
The outsourcer undertakes the following functions: Cost analysis; Demand Management; Sourcing, Selecting and Negotiating with Suppliers; Agreeing on commercial terms; Comprehensive supplier assessment; and estimates of the expected (contractual) Procurement Savings. This type of cooperation is justified for large purchases and can be transformed into the form of coaching.
The client receives:
- Reducing company spend and / or meeting other targets.
- Improved Cash Flow.
- Access to expertise..
- Access to new technologies and services.
- Shorter procurement cycle.
- Development of a network of reliable suppliers.
- Improving compliance with the requirements of the beneficiaries.
The Outsourcer's remuneration assumes a % of the achieved savings or is calculated on the basis of labor costs with reference to the achieved indicators.
The combination of Strategic Outsourcing and Operation Outsourcing results in Full Cycle Outsourcing.
OUTSOURCING CATEGORY MANAGEMENT
This is the most complete form of outsourcing. In fact, a certain category of procurement (usually not strategic) is transferred to external control. It is not only a combination of Strategic Outsourcing and Operation Outsourcing, but also an actual category COST MANAGEMENT. This form implements the control of Demand and Consumption.
The client receives:
- Achievement of indicators for category spend.
- Realized Savings
- Reduced administrative burden.
- Improved Cash Flow.
- Access to expertise.
- Access to new technologies and services.
- Reducing bureaucracy and freeing up internal resources.
- Improving compliance with the requirements of the beneficiaries.
- Reducing risks from suppliers.
- Standardization of specifications and workflows.
The remuneration of the Outsourcer depends on the fulfillment of the assigned tasks and consists of a fixed part and a % of the realized savings.
The overall picture looks like this:
Development of procurement outsourcing in Russia
The Russian market today is very wary of procurement outsourcing, but it must be admitted that interest in this service is gradually growing.
The main barriers are definitely:
- lack of relevant business practices;
- human factors (habits and limiting beliefs, including fear of losing control);
- difficulties in assessing the economic model and its justification.
Read more about what stops Russian companies from using external procurement expertise in the article Procurement outsourcing in Russia – experts meeting - November 2020
The specificity of procurement outsourcing today is that it does not replace the procurement function in the company, but harmoniously complements it. At the same time, the company retains and develops expertise in procurement. Outsourcing is a value-added option.
To understand the need and optimal format for outsourcing, first of all, it is necessary to diagnose procurement processes to identify the characteristics of the organization, development zones, priorities and available resources.
The key to the success of such projects is the benefits that the client receives, and the contractual relationship is based on this. Do not be afraid to entrust your procurement to professionals.